17 Scale part of an audio vector
MATLAB lets you scale multiple elements of a vector by a common factor using indexing. In the command window, type the following:
v = 1:10Suppose we want to scale the middle 3 elements of v by a factor of 0.5; in the command window, type the following:
v(4:6) = 0.5 * v(4:6)Notice that the middle 3 values of v are now equal to half of their original values.
17.1 scaleAudio.m
Using this technique, write a function named scaleAudio that scales part of an audio vector by a factor factor. When the audio vector is played, the parts that were scaled will sound quieter (if factor is between 0 and 1) or louder (if factor is greater than 1).
In scaleAudio it would be convenient to select the part of the audio vector that should be scaled by using a start time and an end time instead of a start index and a stop index.
scaleAudio should satisfy all of the following requirements:
- it should be named
scaleAudio - it should have five input variables
y: the input audio vectorfactor: the scale factortStart: the start time of the selectiontStop: the end time of the selectionfs: the sampling frequency
- it should return one value: an audio vector named
z zshould be equal toyexcept for the values between timetStartandtStopwhich should be equal to the corresponding values inyscaled byfactor- it should have a help documentation comment
This function is easy to implement if you use your function time2index.
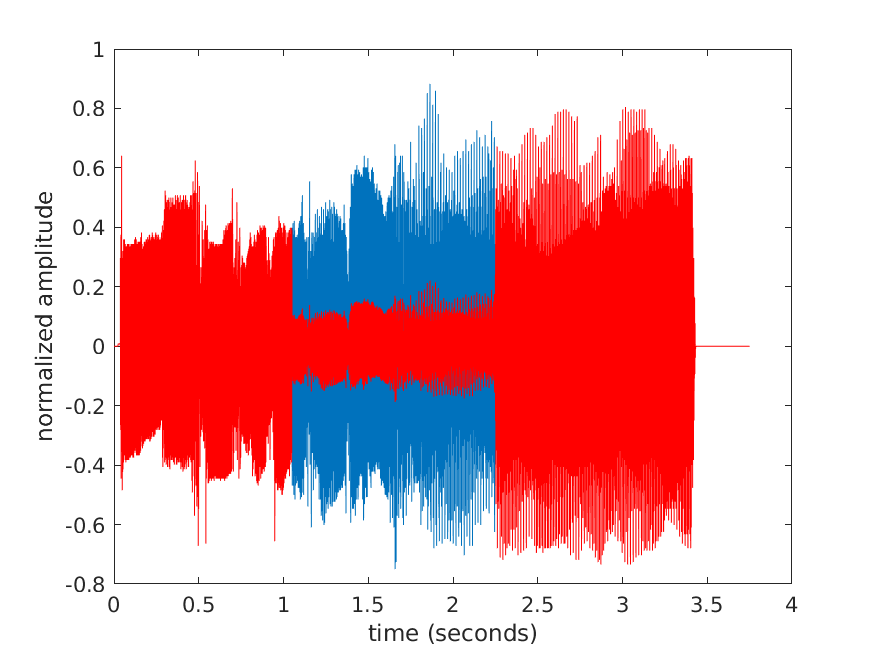
17.2 Use scaleAudio and plot the results
In the MATLAB Command Window type the following:
y = audioread('dspafsx_mono.wav');
fs = 16000;
dt = 1 / fs;
duration = numel(y) / fs;
time = 0:dt:(duration - dt);
plot(time, y)
hold on
z = scaleAudio(y, 0.25, 1.05, 2.25, fs);
plot(time, z, 'r')
xlabel('time (seconds)');
ylabel('normalized amplitude')
hold offIf your scaleAudio function is implemented correctly you should see the following plot: