Variables and their types
A powerful and basic feature of a programming language is the ability to manipulate variables. A variable is a name that refers to a value.
For example, the equation to convert a temperature in Fahrenheit (f) to degrees Centigrade (i.e. c) is:
c = (f - 32) × 5/9
To convert 72 degrees Fahrenheit to centigrade, in Python we might write
# saved in file variable-C2F
# constants
# saved in file variable-C2F
# constants
CONST32 = 32
CONST59 = 5/9
# input is 72 degrees. Change for a different input.
fahrenheit = 72 #
# conversion formula
centigrade = (fahrenheit - CONST32) * CONST59
print(centigrade)
If we run the program python3 variable-C2F.py, then the output at the console is:
22.22222222222222
In the program, fahrenheit and centigrade are variables that point to an object somewhere in the computer's memory (called the the "heap").
Objects
A variable such as fahrenheit points to an object, and every object has:
- an id
- a value
- and a type.
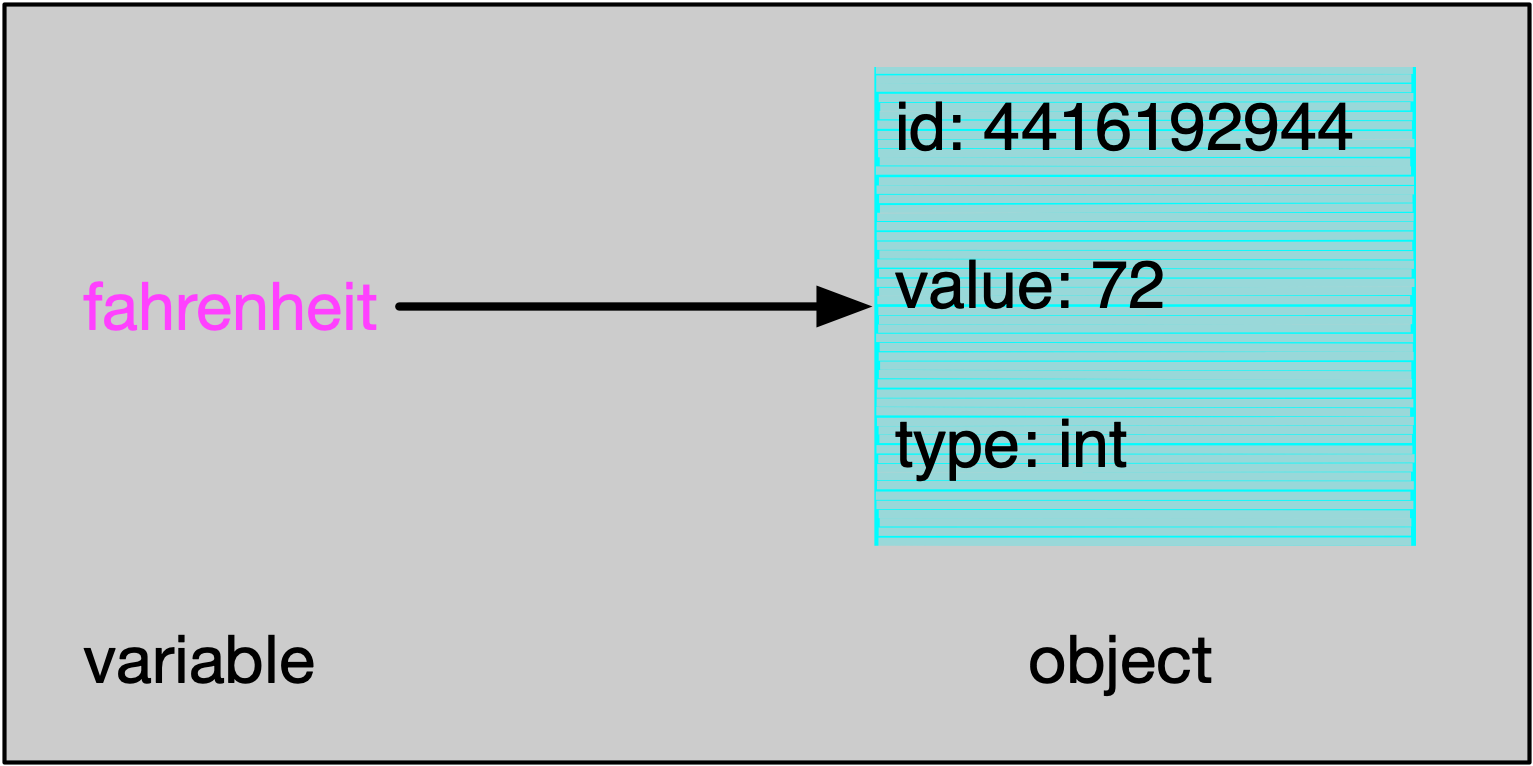
- The identity of an object uniquely identifies where this object is stored in the computer memory.
- The value of the object for
fahrenheitis currently 72 (degrees). When we executeprint(fahrenheit)we obtain the value of this variable. - The type of the varaible
fahrenheitisint(i.e. integer).