Class Binary2
- java.lang.Object
-
- Binary2
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
Comparable<Binary2>
public class Binary2 extends Object implements Comparable<Binary2>
A class that represents a binary (base-2) number. A binary number is made up of one or more binary digits called bits. A bit has a value that is equal to either 0 or 1. An 8-bit binary number is shown below.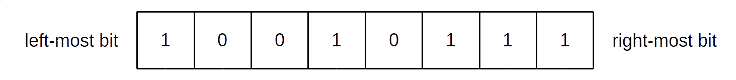
A
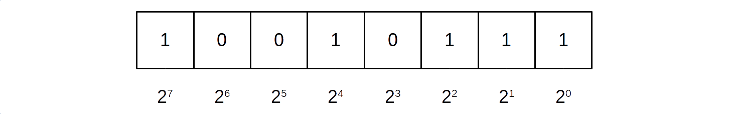
Binarynumber owns the individual bits.To convert a binary number to its decimal (base-10) equivalent, each bit is multiplied by an increasing power of 2 starting from the right-most bit. For example, the decimal equivalent of the 8-bit binary number can be calculated as (1 * 128) + (0 * 64) + (0 * 32) + (1 * 16) + (0 * 8) + (1 * 4) + (1 * 2) + (1 * 1) = 151:
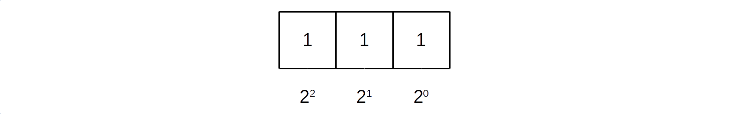
The decimal equivalent of the 3-bit binary number can be calculated as (1 * 4) + (1 * 2) + (1 * 1) = 7:
-
-
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method Description (package private) static intcompare(List<Bit> x, List<Bit> y)Using recursion, compares two lists of digits numerically digit by digit starting from the front of the lists using recursion.intcompareTo(Binary2 other)Compares this binary number to another binary number for order.booleanequals(Object obj)Compares this binary number to an object for equality.BitgetBit(int index)Gets the bit at the given index.List<Bit>getBits()Returns a reference to the list of bits; for testing purposes only.inthashCode()Returns a hash code for this binary number.static voidmain(String[] args)A simple test method.intnumberOfBits()Returns the number of bits in this binary number.Binary2padFront(int n)Returns a new binary number equal to this binary number with n extra binary zeros inserted at the beginning of the number.voidsetLeftmostBit(Bit bit)Sets the leftmost bit by copying the value ofbitinto the leftmost bit.inttoDecimal()Returns the decimal (base 10) value of this binary number as anintvalue.StringtoString()Returns a string representation of this binary number.
-
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
Binary2
public Binary2(Bit bit)
Initializes this binary number to a single digit binary number by copying the specified bit.- Parameters:
bit- the bit to copy
-
Binary2
public Binary2(List<Bit> bits)
Initializes this binary number to have the specified bits. The constructor copies the individual bits into this binary number.- Parameters:
bits- the bits of the binary number- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if bits.size() is less than 1
-
-
Method Detail
-
numberOfBits
public int numberOfBits()
Returns the number of bits in this binary number.- Returns:
- the number of bits in this binary number
-
getBit
public Bit getBit(int index)
Gets the bit at the given index. The returned bit cannot be used to modify this binary number.Index 0 is the index of the left-most bit.
- Parameters:
index- the index of the bit to get- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- if index is out of bounds for this binary number
-
setLeftmostBit
public void setLeftmostBit(Bit bit)
Sets the leftmost bit by copying the value ofbitinto the leftmost bit.- Parameters:
bit- the value of the bit to set
-
toDecimal
public int toDecimal()
Returns the decimal (base 10) value of this binary number as anintvalue. If this binary number has 32 bits or more then the user of this method should expect that the result will be incorrect because of overflow.- Returns:
- the decimal (base 10) value of this binary number
-
padFront
public Binary2 padFront(int n)
Returns a new binary number equal to this binary number with n extra binary zeros inserted at the beginning of the number. For example, if this binary number has the digits0101
then
padFront(4)would return the new binary number00000101
- Parameters:
n- the number of zeros to add to the beginning of the new binary number- Returns:
- a new binary number equal to this binary number with n extra binary zeros inserted at the beginning of the number
-
compareTo
public int compareTo(Binary2 other)
Compares this binary number to another binary number for order. The result is a positive integer, zero, or a negative integer if the decimal value of this number is greater than, equal to, or less that the other binary number.This method does not use
toDecimalto compare the two numbers becausetoDecimalmay overflow the range of int. Instead, it pads the shorter binary number with zeros so that the two numbers have the same number of digits. Then the digits of the two numbers are compared bit by bit.- Specified by:
compareToin interfaceComparable<Binary2>- Parameters:
other- a binary number to compare to this number- Returns:
- a positive integer, zero, or a negative integer if the decimal value of this number is greater than, equal to, or less that the other binary number
-
compare
static int compare(List<Bit> x, List<Bit> y)
Using recursion, compares two lists of digits numerically digit by digit starting from the front of the lists using recursion. Both lists are assumed to be non-empty and to have the same size. Both lists remain unchanged when the method completes.If you interpret the digits of a list as representing the digits of a number then this method determines if the value represented by the digits in
xis equal, less than, or greater than the value represented by the digits iny. For example ifxis the list[0, 1, 0]then
xrepresents the binary number 010. Ifyis the list[0, 1, 1]then
yrepresents the number 011. The value ofcompare(x, y)is a negative value because 010 is less than 011.- Parameters:
x- a list of binary digitsy- a second list of binary digits- Returns:
- the value of 0 if the digits in x are equal to the digits in y; a negative value if the digits in x represent a number that is less than the number represented by the digits in y; a positive value if the digits in x represent a number that is greater than the number represented by the digits in y
- Precondition:
- x.size() == y.size() and x.size() != 0
-
equals
public boolean equals(Object obj)
Compares this binary number to an object for equality. Returns true if and only ifobjis aBinarynumber that represents the same decimal value as this number.This method does not use
toDecimalto compare the binary numbers. Instead, it usescompareToto check for equality (compareTois consistent withequals).
-
toString
public String toString()
Returns a string representation of this binary number. The returned string is made up of the bit values (0 or 1) of the number from the left-most bit to the right-most bit.
-
hashCode
public int hashCode()
Returns a hash code for this binary number.
-
getBits
public List<Bit> getBits()
Returns a reference to the list of bits; for testing purposes only.- Returns:
- a reference to the list of bits of this binary number
-
main
public static void main(String[] args)
A simple test method.- Parameters:
args- not used
-
-