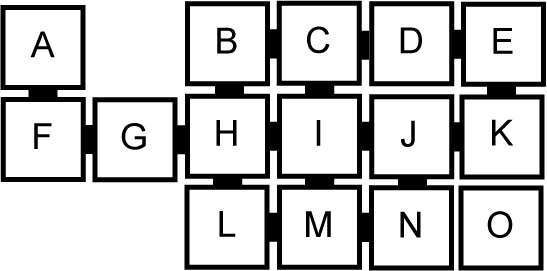
Take your solution from Part 1 and change line 17 (see below) to read start = MazeRoom.buildCyclicMaze();. This generates the maze illustrated below. Run your solution and try to find a path from "I" to "L" or "N" or "B". What happens?

The cycles (i.e., loops) in the maze can cause infinite recursive calls. To solve this issue, we can use a set to keep track of the rooms we have already visited. If a room is already in the set, we have already been there, so you do not need to search it (again).
Use the following code to create a class named "MazeSolver2":
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Given a MazeRoom and a room name, the search facility of this class
* will return a path to the desired room, if one exists.
*
* The search will succeed, even if the maze contains cycles (i.e., loops).
*/
public class MazeSolver2
{
private MazeRoom start;
/**
* Initializes this object.
*/
public MazeSolver2()
{
start = MazeRoom.buildCyclicMaze();
}
/**
* Provides access to the maze entrance.
* @return the entrance to the maze.
*/
public MazeRoom getEntrance()
{
return start;
}
/**
* Finds a path from the current room in the maze to the room with the name
* provided by goal, if one exists.
* @param current the current room being searched.
* @param goal the name of the destination room.
* @param visited all the rooms already searched.
* @return a path from the current room to the goal (e.g., "A->F->G"), or
* null if no path exists.
*/
public String findPath(MazeRoom current, String goal,
HashSet<MazeRoom> visited)
{
// Your code goes here...
// Hint: When you enter a room (i.e., current) search each connected,
// non-null room (using goNorth(), goSouth(), goEast(), and goWest()),
// except ones that are already in the set. Stop when the current room's
// name is the goal.
;
}
/**
* Used to test the functionality of this class.
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PrintStream out = System.out;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
MazeSolver2 ms = new MazeSolver2();
MazeRoom start = ms.getEntrance();
out.println("The entrance to the maze is room " + start.getName());
out.print("Enter the destination room name: ");
String goal = in.next();
String path = ms.findPath(start, goal, new HashSet<MazeRoom>());
out.print("\nThe path from " + start.getName() + " to " + goal + " is ");
out.println(path == null ? "non existent!" : (path + "."));
}
}
Implement the findPath method and use this code to test your class. Ensure that you know what this code does and how it works.